Chances are, earwax and its accumulation haven’t been subjects of significant contemplation for you, except perhaps during ear hygiene routines. Still, it’s essential to have an understanding of its purpose and how it forms.
What initiates the accumulation of earwax?
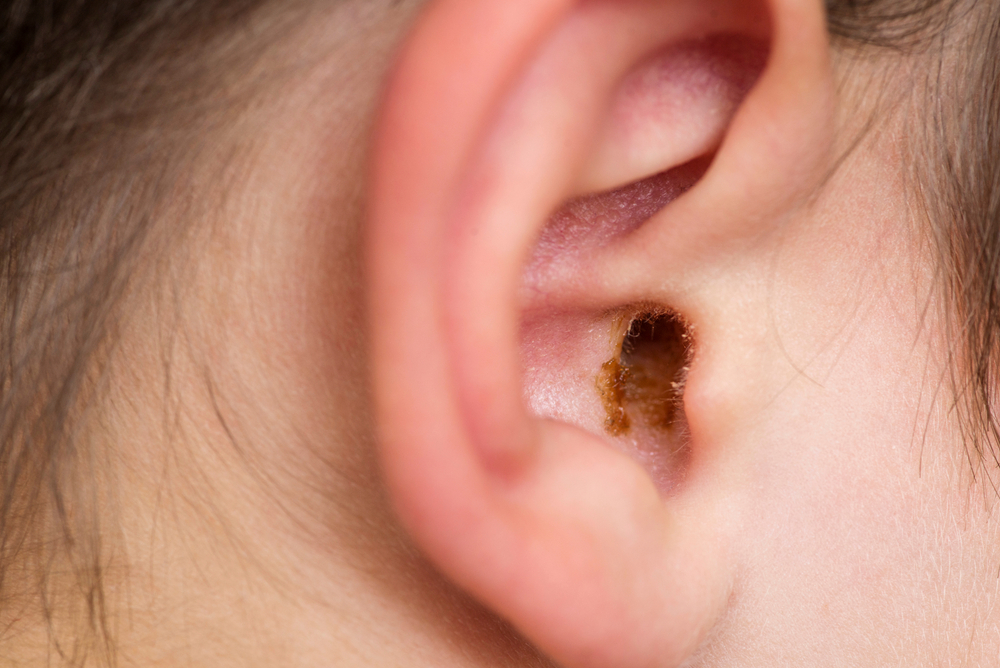
Earwax, also scientifically called cerumen, is composed of a mix of sweat, skin particles, hair, debris, and ceruminous gland secretions. Earwax will appear as a waxy substance that will typically be yellow, orange, brown, or even grey.
While the production amount of earwax differs from individual to individual, adults typically produce less earwax than children. Furthermore, adult earwax tends to be darker and harder compared to that of children.
Earwax passes the outer ear canal naturally, eventually reaching the ear opening, where it either self-expels or gets washed out when you bathe.
Why is earwax important?
Here are a few crucial functions that earwax serves:
- Protecting and moisturizing the skin lining the ear canal, thereby preventing dryness and itchiness.
- Fending off possible infections that may develop within the ear canal.
- Acting as a protective barricade against outside irritants such as dirt, dust, and other foreign particles before they infiltrate deeper into the ear.
Blockages caused by earwax
Typically, there’s no crucial need to remove earwax from your ears unless it becomes impacted, a common issue linked to earwax. In some cases, earwax is unable to easily get to the opening of the ear as a result of narrow or unusually shaped ear canals.
Improper ear hygiene practices, such as using cotton swabs or bobby pins, can inadvertently jam wax deeper into the ear canal.
Earwax obstructions are often experienced by individuals who often use earplugs, earbuds, or hearing aids.
How is hearing affected by too much earwax?
The presence of earwax blockages may yield slight discomfort and dampen auditory health.
In addition, considerable accumulations of earwax can induce tinnitus, a sensation of ringing in the ears.
Untreated earwax blockages may escalate into middle ear infections, perforated eardrums, or enduring hearing loss as a result of acoustic trauma.
Addressing impacted earwax
It’s essential that you get in touch with us as soon as you can if you think your ears are blocked by earwax. Depending on the extent of the blockage, you may be advised to make use of over-the-counter wax softening drops or a bulb syringe for gentle irrigation to relieve the condition.
Call us right away if you need some assistance with an earwax blockage.